Pearly Penile Papules (PPP)

Table of contents
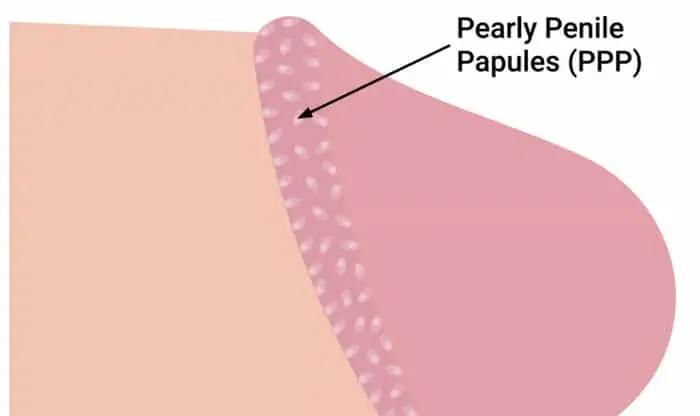
definition
Pearly penile papules (PPP) are a common skin condition characterized by small, pearl-like or white papules that appear on the edge of the glans penis (coronal sulcus) or the lower part of the glans. These papules are usually arranged in a regular pattern and resemble small granules or pearls in appearance, hence the name. PPP is a benign, non-contagious physiological variation that usually does not pose a threat to health, but may cause psychological or aesthetic concerns due to its appearance. This condition is more common in men, especially young men aged 20 to 40.

symptom
The main symptoms of penile pearly papules include:
- Appearance featuresPapules are small, raised bumps, 1-3 mm in size, usually white, pink, or skin-colored, arranged neatly in a ring or semi-ring pattern along the coronal sulcus of the glans penis. The surface of the papules is smooth, without ulceration or discharge.
- asymptomaticPPP usually does not cause pain, itching, burning or other discomfort.
- stabilityThe size and number of papules usually remain stable over a long period of time and do not spread or worsen on their own.
- Non-infectiousPPP is not a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and cannot be transmitted to others through sexual contact.
Because PPP can look similar to other skin lesions such as genital warts, some patients may mistakenly believe they have contracted a sexually transmitted infection, leading to anxiety.

Causes
The exact cause of penile pearly papules is not yet fully determined by the medical community, but the following are some generally accepted views:
- Physiological variationPPP is considered a normal skin variation that may be related to genetics or individual constitution. It is not a disease, but rather a natural manifestation of skin tissue.
- Sebaceous gland relatedSome studies suggest that PPP may be related to the abnormal proliferation of sebaceous glands or eccrine glands, which may become more prominent after puberty due to hormonal changes.
- Genetic factorsPPP is more common in certain ethnic groups (such as African American or uncircumcised men), suggesting a possible genetic predisposition.
- Non-pathologicalPPP is not directly related to infection, hygiene, or sexual behavior, nor is it caused by viruses or bacteria.
It is worth noting that the incidence of PPP is slightly higher in uncircumcised men, with approximately 20-30% of men having %, while the incidence is slightly lower in circumcised men.

diagnosis
Diagnosis of penile pearly papules is usually made by a professional physician (dermatologist or urologist) using the following methods:
- Visual examinationThe doctor will make a preliminary diagnosis based on the appearance, arrangement, and location of the papules. A typical characteristic of PPP is small, regularly arranged papules without inflammation or ulceration.
- Medical history inquiryThe doctor will ask the patient about their symptoms, medical history, and sexual history to rule out other possible diseases.
- Differential diagnosisBecause PPP can resemble lesions such as genital warts (caused by human papillomavirus, HPV), Fordyce spots, or lichen planus, a differential diagnosis may be necessary. If required, a skin biopsy or HPV testing may be performed to rule out other causes.
- No routine check requiredThe diagnosis of PPP usually does not require blood tests or other invasive examinations unless there are other symptoms of suspected lesions.
If a patient is concerned about PPP, it is recommended to seek professional medical evaluation as soon as possible to obtain a correct diagnosis and relieve psychological stress.

treat
Penile pearly papules are benign and harmless and usually do not require treatment. However, if a patient wishes to remove PPPs due to appearance or psychological factors, the following treatment options may be considered:
- Non-surgical treatment:
- Observation and psychological supportMost doctors would advise patients to accept PPP as a normal physiological phenomenon to avoid unnecessary treatment. Psychological counseling can help relieve anxiety.
- Topical medicationThere is currently no specific drug treatment for PPP, and applying steroids or other ointments is usually ineffective.
- Surgical or invasive treatment:
- Carbon dioxide laser (CO2 laser)This is the most commonly used treatment method, which can precisely remove papules, has a short recovery period, and is highly effective.
- ElectrodesiccationBurning papules with electric current is suitable for small lesions, but there may be a slight risk of scarring.
- CryotherapyUsing liquid nitrogen to cryotherapy papules is suitable for the treatment of a small number of papules.
- Surgical resectionUse only in very rare cases, as it may leave scars or affect appearance.
- PrecautionsAll treatments should be performed by a professional physician. Avoid using chemical agents or non-medical methods (such as toothpaste or acidic substances) to remove papules yourself, as this may cause infection or damage.
Before treatment, patients should fully discuss the risks and benefits with their doctor, especially the possible scarring or pigmentation changes that may result from the treatment.

Trying unproven home remedies
toothpaste
Apply toothpaste to the pimples once a day. While this method has not been researched and proven effective, some men claim it works. To do this, apply toothpaste to the pimple with your fingertip and leave it on for 5 to 10 minutes. Then, rinse the toothpaste off thoroughly.
Try doing this before showering or bathing.
Repeat this process daily for 4 to 6 weeks to see if there is any improvement.
Please remember that experts do not recommend using toothpaste on the penis.

castor oil
Try applying castor oil to the papules once a day. Some men have also seen results after applying castor oil to their PPPs daily for several weeks. Apply the castor oil to your PPPs with a cotton ball or cotton swab. Leave it on for 5 to 10 minutes, then rinse it off.
Do this once a day for 4 to 6 weeks and see if the papules change.
While castor oil won't harm your penis, experts warn that it may not be effective for papules.

Fresh lemon juice
Apply fresh lemon juice to the pimples daily. Although not proven, some men do use lemon juice as a home remedy for PPP. Squeeze the lemon to extract the juice. Then, apply the juice to the PPP with a cotton ball. Let the juice sit for 5 to 10 minutes, then rinse thoroughly.
Repeat this treatment daily for 4 to 6 weeks to observe whether your PPP improves.
The sugar and acid in lemon juice may harm your penis. Experts do not recommend applying the juice to the genitals.

Eucalyptus oil
Try applying diluted eucalyptus oil to the pimples once a day. Some men have found eucalyptus oil effective in treating PPP, so you may also consider this option. Dilute a few drops of eucalyptus oil in one tablespoon (15 ml) of carrier oil, such as almond oil or baby oil. Then, dip a cotton swab in the oil and apply it to the PPP. Leave the oil on the penis throughout the day.
Repeat this treatment daily for 4 to 6 weeks to see if it helps.
Undiluted essential oils can cause skin irritation and allergic reactions. Exercise caution when applying essential oils to the genitals.

prevention
Since penile pearly penile papules are a physiological variation, their occurrence cannot be completely prevented. However, the following suggestions can help reduce related discomfort:
- Maintain good hygieneRegularly clean the penile area and keep it dry to avoid misunderstandings or discomfort caused by insufficient cleaning.
- Avoid misdiagnosisIf you find similar papules, you should consult a professional doctor in time to avoid self-diagnosing them as sexually transmitted diseases or other diseases.
- Mental health managementUnderstand the positive aspects of PPP to reduce unnecessary psychological stress. If needed, seek psychological counseling or support groups.
- Healthy LifestyleAlthough PPP is not directly related to lifestyle, a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding excessive stress contribute to overall health.

Common Questions and Myths
- Is PPP contagious? No, PPP is not a sexually transmitted disease and is unrelated to sexual activity.
- Will PPP disappear on its own? PPP may become less significant with age in some individuals, but in most cases it will persist for a long time.
- How to distinguish between genital warts (PPP) and condyloma acuminata (genital warts)? Genital warts typically have an irregular appearance, may be accompanied by itching or discomfort, and are associated with HPV infection, requiring professional diagnosis for differentiation.

in conclusion
Penile pearly penile papules are a common benign skin lesion that is harmless and requires no special treatment. For most patients, understanding its non-contagious and non-pathological nature helps alleviate psychological stress. If treatment is considered due to appearance concerns, it should be performed at a reputable medical institution by a qualified physician. With proper diagnosis and appropriate psychological support, patients can better accept and manage this common condition.
Further reading:



![[有片]把與生俱來的「好色」,用以點燃事業的雄心](https://findgirl.org/storage/2025/11/有片把與生俱來的「好色」,用以點燃事業的雄心-300x225.webp)


-300x225.webp)
