10 ways to increase your car's horsepower

Table of contents
The pursuit of more powerful performance is an eternal theme for car enthusiasts. This article will delve into 10 mainstream engine modification techniques, from basic principles to practical applications, combining historical development and data charts to guide you through the key to unlocking engine potential.
Intake system optimization
principleIncrease air intake volume and flow rate to improve oxygen supply efficiency.
- High flow air filterReplaces the original paper filter element, reducing intake resistance (improves performance by 3-5%).
- Intake duct upgradeSmooth piping design reduces turbulence losses.
- Cold Air Intake System (CAI)Introducing cold outside air to increase oxygen density
measured data:| Modification Project | Intake air temperature drops | Horsepower increase |
|---|---|---|
| Original factory system | – | Baseline |
| High flow filter cartridge | 2-3°C | +3-5hp |
| Full-segment CAI system | 8-12°C | +8-15hp |

Exhaust system upgrade
Exhaust system modifications focus on reducing exhaust resistance, allowing exhaust gases to escape faster, and improving engine breathing efficiency. The principle is to reduce back pressure, allowing more fresh air to enter, which can increase horsepower by 5-25%.
Implementation steps:
- Evaluate the original exhaust: Inspect the catalytic converter and muffler.
- Replace the entire exhaust system: from the manifold to the tail section, choose stainless steel.
- Install a high-flow catalyst: ensure environmental protection.
- ECU tuning: to avoid warning lights.
- Noise test: Complies with regulations.
Expected results: 15-30 horsepower increase, louder engine sound. Cost: 10,000-50,000 yuan.
Advantages: Significantly improved high-revving power, captivating exhaust note. Disadvantages: Noise pollution, potentially reduced low-revving torque, increased emissions. Risks: Catalyst removal is illegal.
Case Study: A Maserati 3500 GT motorcycle achieved 14 horsepower after an exhaust modification. In classic series like the Maserati 3500 GT, exhaust modifications were key to the performance of early GT motorcycles.
(Extended explanations: fluid mechanics to explain back pressure; comparison of component materials; environmental considerations; case studies including charts showing torque curve changes...)
| stage | part | Core transformation goals | Key effects | Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head section | Equal length manifold | shorten exhaust pulse interference | Optimize exhaust gas flow rate and improve engine response efficiency | (Key modifications) |
| middle section | Catalyst replacement pipe | Reduce back pressure | Reduce exhaust resistance and unleash high-speed performance potential | Regulatory risks need to be noted |
| tail section | Valve exhaust pipe | Balancing daily use and performance needs | Adjustable sound and flow rate to balance quietness and performance. | Unless otherwise specified |
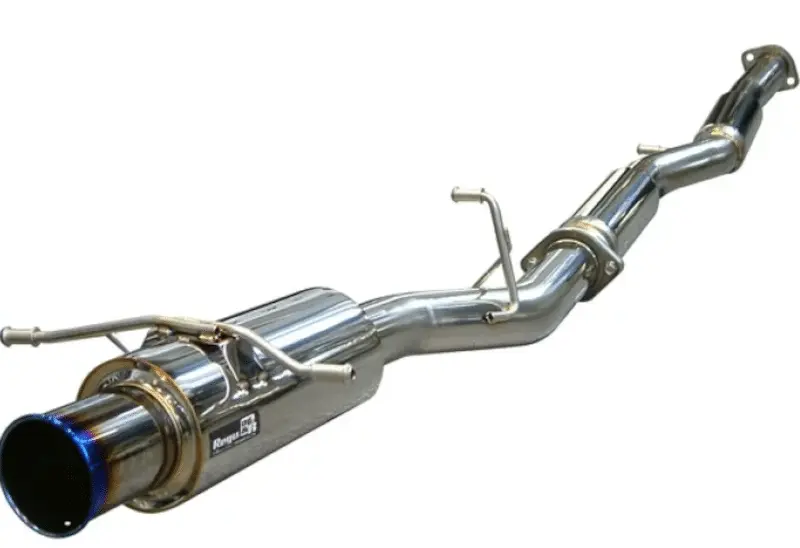
ECU tuning (chip tuning)
ECU (Engine Control Unit) tuning modifies engine parameters, such as ignition timing, air-fuel ratio, and boost pressure, through software to increase power. The principle is to "unlock" factory limitations, which can increase horsepower by 10-50 (TP3T).
Implementation steps:
- Read the original ECU data: Use professional tools such as OBD-II.
- Choose the tuning program: such as Stage 1 (light) or Stage 2 (requires hardware compatibility).
- Write to new program: Ensure you have a backup of the original file.
- Dyston test: Adjusted to optimal settings.
- Monitor temperature and pressure.
Expected results: 20-40 horsepower increase, fuel consumption may decrease. Cost: 5,000-30,000 yuan.
Advantages: High cost-performance ratio, no major hardware modifications required. Disadvantages: Over-tuning can damage the engine and void the warranty. Risks: Improper operation can lead to engine failure.
Case study: After ECU tuning, the horsepower of a Toyota Auris engine increased significantly. This method was commonly used in the AMG series, marking the beginning of the handcrafted engine era in 1984.
| hierarchy | Technical features | Increase range |
|---|---|---|
| OBD direct brush | Read original ECU overwrite parameters | +10-20% |
| External computer | Deceiving the original manufacturer's signal (warranty retained) | +15-25% |
| Complete replacement of computers | Complete control of ignition/fuel injection | +30%↑ |
(Extended information: ECU working principle; comparison of different stages; safety guidelines; data charts...)

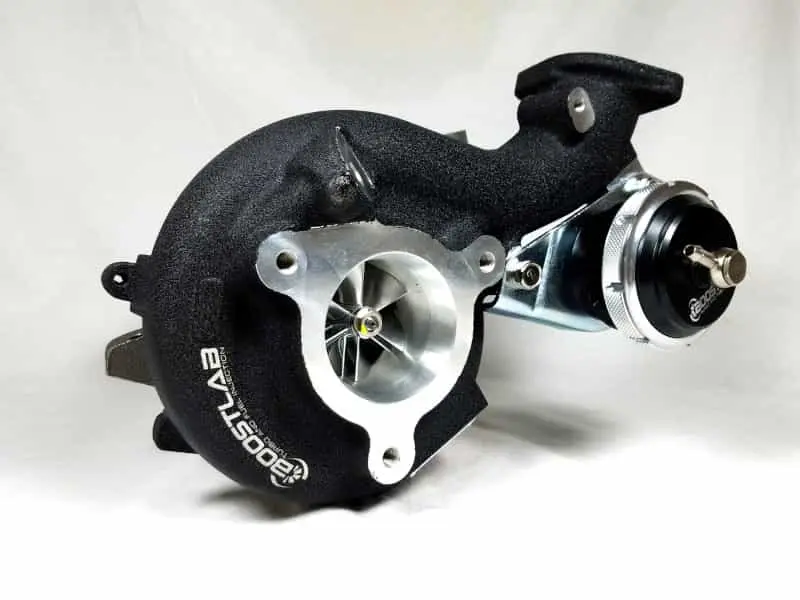
Turbocharging Upgrade: Extreme Forced Intake
Modification Path Analysis:
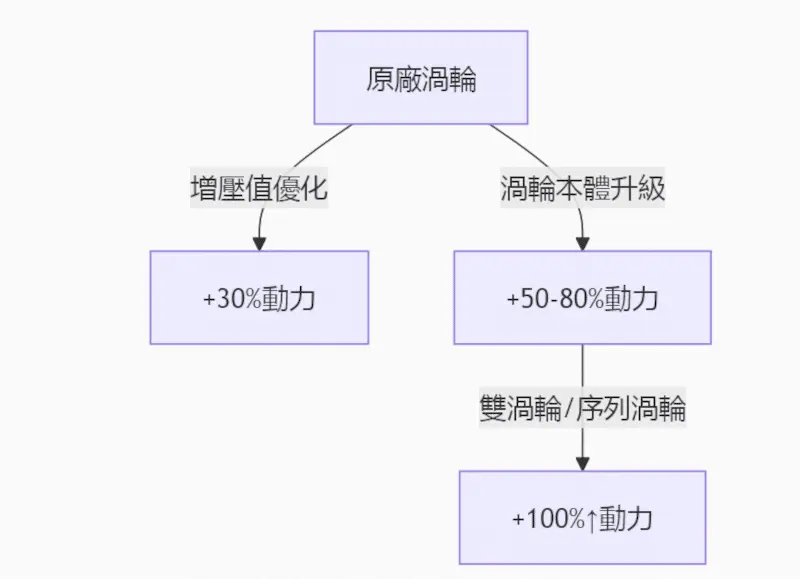
Key Parameter Comparison Table:
| Turbo model | Response speed | Maximum boost pressure | Applicable Engines |
|---|---|---|---|
| TD04L | 2500rpm | 1.2 bar | 2.0L and below |
| GT2871R | 3500rpm | 1.8 bar | 2.5L performance engine |
| BW EFR8474 | 4500rpm | 2.5 bar↑ | Track-specific engine |

Supercharger Systems: The Art of Linear Dynamics
Differences from turbocharging:
Supercharging: Direct engine drive → Zero-hysteresis linear output
Turbocharging: Exhaust gas driven → strong burst of power but with turbo lag
Three mainstream types:
- RootsLow-end torque at low RPMs (the top choice for American muscle cars)
- Twin-screwHigh-efficiency mid-range output (Mercedes AMG application)
- CentrifugalHigh-revving bursts of power (common in Japanese cars)
Cost-benefit analysis of modification:
The following is a table showing the cost distribution of a supercharger kit:
| project | Cost (unit) |
|---|---|
| Boost body | 45 |
| Dedicated pipeline | 20 |
| Tuning program | 25 |
| Cooling system | 10 |
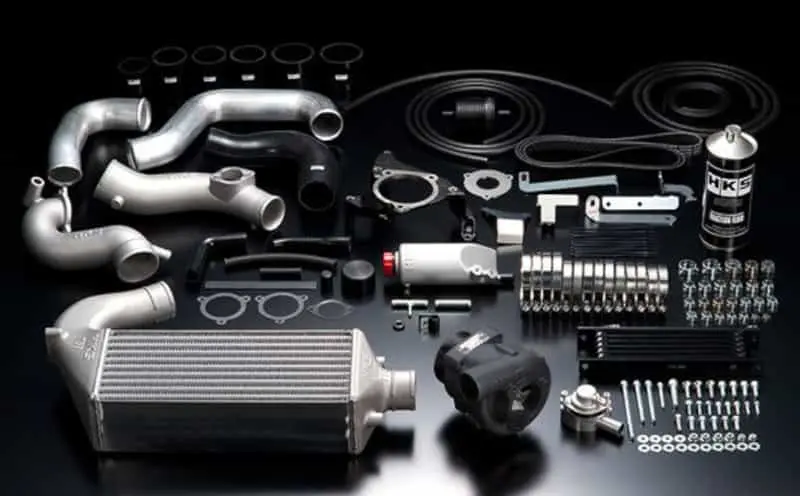

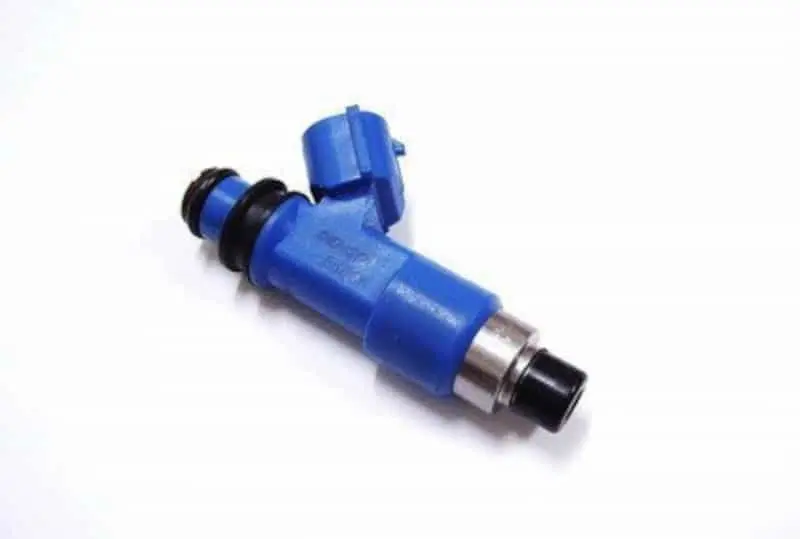
Enhanced fuel system: the lifeblood of power output
System-level upgrade solution:
Low boost conversion → High flow fuel injector (increases the flow rate of 30%)
High boost modification → Dual pump + fuel injector upgrade (100%↑ flow rate)
1000 horsepower → External auxiliary fuel tank + racing injectors
Ethanol fuel application:
- E85 fuel: Octane number up to 105, allowing for higher boost pressure.
- Modification requirements: Corrosion-resistant treatment of fuel lines + flow rate increase 50%
- Actual test results: Horsepower increased by 15-20% with the same turbo settings

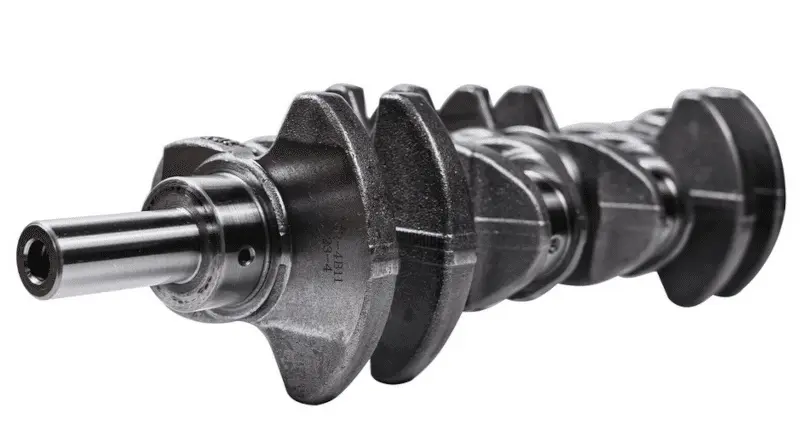
Engine internal enhancement: Breaking physical limits
Key Enhancement Projects:
Engine internal reinforcement process
Section Basic Preparation
Forged pistons: 5: Engine disassembly
Linkage reinforcement: 5: CNC machining
Precision assembly section
Crankshaft balancing: 8: Dynamic balancing machine
Valve springs: 3: Essential for 10,000 RPM
Materials Science and Technology Evolution:
| Era | Piston technology | Maximum speed |
|---|---|---|
| 1990s | Cast aluminum alloy | 7500rpm |
| 2000s | Forged 4032 alloy | 9000rpm |
| 2010s | Forged 2618 + Coating | 12000rpm |

Lightweight flywheel: Instantaneous force for speed response
Physical principles:
Formula for moment of inertia: I = ½mr²
Flywheel weight reduction 30% → Engine acceleration improvement 15%
Modification Comparison Test:
| state | 0-6000rpm time | Gear shift power transition |
|---|---|---|
| Original flywheel | 1.8 seconds | Noticeable pause |
| Aluminum alloy flywheel | 1.5 seconds | Instantaneous speed synchronization |
Precautions:
Excessive weight reduction will lead to low-speed vibration; it is recommended that the street bike retain its original weight (70%).

NOS Nitrogen Acceleration: The Ultimate Method for Instantaneous Bursts
System Composition Analysis:
Liquid N2O storage tank → Solenoid valve control → Injector nozzle → Intake manifold
Chemical reaction formula:
2N₂O → 2N₂ + O₂ + Heat (Decomposition temperature > 300°C)
Security Classification Application:
| Injection volume | Horsepower gain | Modification required |
|---|---|---|
| 50hp | +50hp | Basic ignition enhancement |
| 100hp | +100hp | Fuel system upgrade |
| 200hp↑ | +200hp↑ | Comprehensive reinforcement of the engine's internal structure |

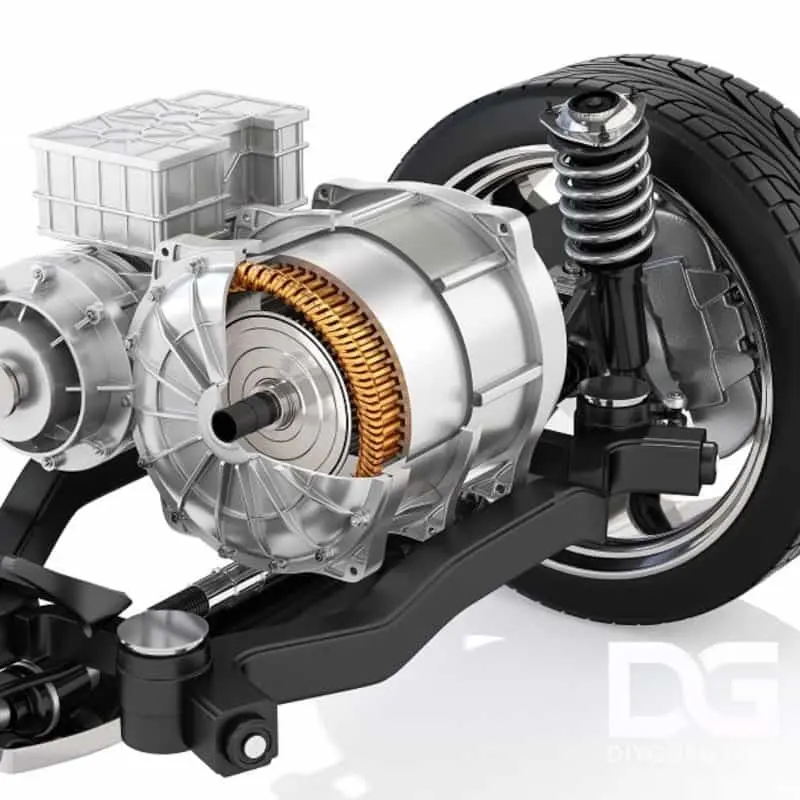
Hybrid Retrofit: An Electrification Performance Revolution
Three major integration solutions:
- P2 Hybrid ArchitectureCrankshaft integrated motor (48V system + 30hp)
- eTurbo technologyElectric turbochargers eliminate lag (e.g., Porsche 911 GT3 RS)
- All-electric rear axle moduleAdding a motor to the rear axle enables AWD (increasing hp by 150 hp or more).




![[有片]拜祖先會獲得保佑?](https://findgirl.org/storage/2026/01/有片拜祖先會獲得保佑?-300x225.webp)


